Smart farming technology is revolutionizing livestock farming by integrating advanced tools like artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and precision agriculture. These innovations address critical challenges such as sustainability, animal welfare, and operational efficiency, paving the way for a more productive and eco-friendly future in agriculture.
Data-Driven Decisions with IoT and Analytics
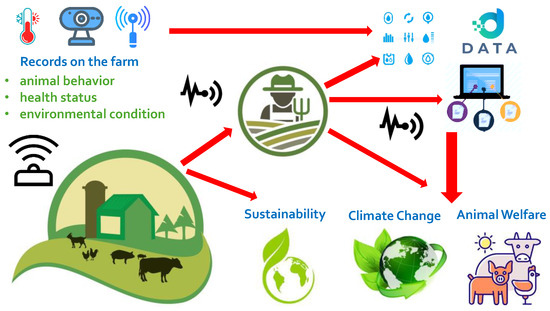
IoT devices and sensors are transforming livestock management by providing real-time data on factors like:
Feed Quality: Tracking nutrient levels to optimize feeding schedules.
Environmental Conditions: Monitoring temperature and humidity for improved animal comfort.
Health Metrics: Early detection of illnesses through biometric sensors.
By analyzing this data, farmers can adopt precision agriculture practices that enhance productivity, reduce waste, and improve overall farm sustainability.
Revolutionizing Farming with Artificial Intelligence

AI and machine learning (ML) are empowering farmers with predictive tools to:
Detect Diseases Early: Analyze behavior and physiological changes to predict health issues.
Automate Routine Tasks: Use AI to manage feeding schedules and track animal movements.
Enhance Breeding Programs: Optimize genetic traits for higher yields and disease resistance.
These tools not only improve efficiency but also ensure better care for livestock.
Ensuring Transparency with Blockchain

Blockchain technology is redefining transparency in livestock farming by creating immutable records of:
Animal Welfare Practices: Verifying ethical treatment of animals.
Product Authenticity: Certifying claims like “organic” or “antibiotic-free.”
Supply Chain Traceability: Tracking livestock and products from farm to consumer.
This fosters consumer trust while aiding compliance with regulatory standards.
Drones and Satellite Technology in Livestock Management

Drones and satellites are game-changers in farm monitoring, offering benefits such as:
Efficient Pasture Management: Real-time mapping of grazing areas.
Hazard Detection: Identifying potential risks like flooding or fires.
Livestock Tracking: Monitoring herds across vast terrains.
These technologies reduce labor costs while improving productivity and safety.
Automated Feeding Systems for Precision Nutrition

Automated feeding systems use data to tailor nutrition plans for livestock, ensuring:
Optimized Growth: Adjusting feed quantities based on individual needs.
Reduced Waste: Eliminating overfeeding or underfeeding.
Labor Efficiency: Reducing manual effort with automated processes.
By providing consistent and accurate feeding, these systems contribute to healthier livestock and higher yields.
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering

Advancements in biotechnology are addressing global food security with innovations like:
Disease-Resistant Livestock: Developing animals with enhanced immunity.
Improved Productivity: Achieving higher milk and meat yields through genetic modifications.
Sustainable Practices: Reducing resource use while maintaining output.
Despite ethical debates, these technologies offer promising solutions to modern challenges in agriculture.
Online Marketplaces: A Digital Revolution for Farmers
E-commerce platforms are transforming livestock sales by:
Connecting Farmers and Buyers: Enabling direct transactions without intermediaries.
Providing Certifications: Digital proof of quality and health standards.
Expanding Market Access: Helping small-scale farmers reach global buyers.
These platforms streamline the buying process while promoting fair pricing.
Sustainable Practices for a Greener Future

Sustainability is at the heart of smart farming technology, with innovations such as:
Waste-to-Energy Systems: Converting livestock waste into renewable energy.
Water Recycling: Reducing water usage through advanced filtration systems.
Regenerative Agriculture: Restoring soil health for long-term productivity.
By adopting these practices, farmers can reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining profitability.
Challenges in Adopting Smart Farming Technology

While promising, smart farming faces barriers such as:
High Initial Costs: Advanced systems require significant investment.
Skill Gaps: Farmers need training to utilize new technologies effectively.
Data Security Risks: Protecting sensitive information from cyber threats.
Government support, infrastructure development, and accessible financing are crucial to overcoming these challenges.
Road Ahead: A Digital Revolution in Livestock Farming
Smart farming technology is reshaping the livestock industry by integrating innovation, sustainability, and efficiency. From AI-driven disease detection to blockchain-enabled transparency, these advancements offer unparalleled benefits for farmers and consumers alike.
As adoption grows, the future of livestock farming promises to be more sustainable, productive, and ethically sound. With continued investment and innovation, the sector is poised to meet the demands of a growing global population while protecting the environment.
Also Read: Agri App ‘UgAi’ Launched for Farmers Access to Fertilizers



