Sleeping Late Cause Diabetes, according to a recent study presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes annual meeting, highlighting a concerning link between poor sleep habits and the risk of developing the condition. Individuals who stay up late and maintain an active night schedule have a staggering 50% higher risk of developing type 1 vs type 2 diabetes. This research, part of the Netherlands Epidemiology of Obesity study, involved over 5,000 participants classified as early risers, intermediates, and late risers.
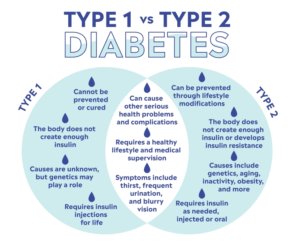
The findings indicate that night owls are significantly more prone to metabolic disorders, including diabetes. Lead researcher Jeroen van der Velde from Leiden University Medical Centre noted that this increased risk stems from a misalignment between the body’s natural circadian rhythm and societal expectations. Such misalignment disrupts metabolic functions, heightening the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
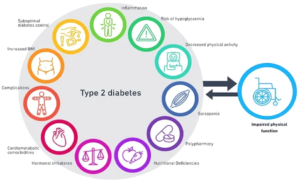
“People with a late chronotype tend to have higher body fat, including visceral and liver fat, contributing to their greater risk,” van der Velde explained. Night owls also exhibit higher body mass indexes and larger waist circumferences, both contributing factors to diabetes risk.

How Sleeping Late Causes Diabetes and Strategies to Mitigate the Risks
However, the study suggests that adopting healthy lifestyle habits could mitigate these risks. Here are some effective strategies for night owls to improve their metabolic health:
1. Establish Consistent Sleep Patterns to Reduce Diabetes Risk

Night owls often suffer from poor-quality sleep due to irregular schedules. Studies show that sleeping late disrupts the body’s circadian rhythm, which increases the risks of type 2 diabetes. Aiming for a consistent bedtime of 7-9 hours of restful sleep can enhance metabolic health and decrease the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease.
2. Prioritize Early Dinner and Regular Exercise

Late-night eating is linked to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Night owls should focus on having dinner earlier to allow ample digestion time before bed. Incorporating regular exercise, such as walking, yoga, or swimming, can help regulate blood sugar levels and maintain metabolic health.
3. Stay Hydrated for Better Blood Sugar Management

Dehydration can cause blood sugar spikes, increasing diabetes risk. Night owls need to drink at least 8 glasses of water daily to maintain balanced blood sugar levels, supporting overall health and metabolic functions.
4. Adopt a Balanced Diet Rich in Fiber and Protein

Late-night snacking can lead to weight gain and metabolic issues. A balanced diet rich in fiber, protein, healthy fats, and essential vitamins is crucial for night owls to stay full and avoid unhealthy cravings, thereby regulating blood sugar levels and supporting overall health.
5. Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking

Night owls are often more likely to smoke and consume alcohol, both of which contribute to a higher risk of type 2 diabetes. Reducing these habits can significantly lower diabetes risk and improve metabolic health.
6. Manage Stress with Mindfulness Techniques

Chronic stress can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Night owls may experience higher stress due to irregular schedules. Incorporating mindfulness, yoga, or meditation can help manage stress levels and prevent blood sugar spikes.
Also Read: Managing Children’s Screen Time Addiction
By adopting these healthy lifestyle habits, night owls can significantly reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and enhance their overall metabolic health.


